|



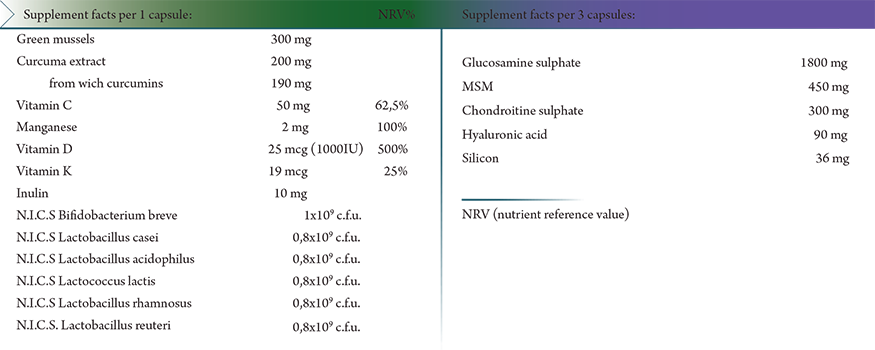
Glucosamine is an amino sugar in the group of nitrogen-containing carbohydrates. It is one of the most abundant monosaccharides in nature and is found in bacteria, fungi, plants and vertebrates. In humans, glucosamine is an important structural component of bones, joints and cartilage.

Persons allergic to shellfish and/or crustaceans should not take this product.
Chondroitin is an organic compound belonging to the group of glucosaminoglycans. It is a chain of alternating sugar molecules with more hundred elements that occurs naturally in the human body as well. The combination of chondroitin and certain mineral salts makes chondroitin sulphate, a polysaccharide found in living organisms, an important structural component of cartilage tissue, a basic constituent of the intercellular structure of cartilage tissue and an important component of joint metabolism.
Dimethylsulfone or methylsulfonylmethane (MSM for short) is an organosulfur compound, present in all living organisms. It is a chemically neutral, colourless, solid due to the sulphonyl functional group. It is found in its natural form in some fresh fruits, vegetables, fish and cereals, milk, tea and coffee preparations. However, MSM content is reduced during processing and heating.
The hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan, hyaluronate) is a natural big molecular carbohydrate which can be found in all tissues. In the human body it mostly has a water-binding role. In the joints and muscles it has a lubricating function.
Silicon is the second most abundant element on Earth. It is a grey, lustrous, semi-metallic substance. It is essential for living cells and can be found in many plants, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, spinach, rice and bamboo, in a form that can be used by the human body. The average human body contains 1.4 g of silicon. It is mostly found in connective tissues, bones, cartilage and skin. It plays an important role in the structure of connective tissues, making the body's tissues extremely elastic.
The green-lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus) is native to New Zealand, has a distinctive dark green/brownish shell, and can grow to 240 mm in length. New Zealand green mussels are considered the best source of glucosamine, glycosaminoglycans, which are the building blocks of articular cartilage and synovial fluids, but are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. It has important biological and physiological functions and all the positive properties of glucosamine and is therefore widely used in medicine.
Curcuma or turmeric is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant cultivated in India and Indonesia. Its root is canaliculate. Inside it has an orange, pulpy consistency. In temperate zones turmeric can not be grown in the garden. In the 1870s chemists noticed that the orange colored curcuma root changed its color to red due to alkali. This recognition led to the development of ˝curcuma paper˝ which was widely used in chemical analysis as an indicator of acidity and alkalinity at the end of the 19th century. Later litmus paper took over this task.
In European and American cuisine turmeric is relatively new, but it has a rich history in its homeland India where its well known and has been consumed for thousands of years. Curcuma enriches not only cuisine, but also herbal medicine. In India's traditional Ayurvedic medicine, turmeric is a symbol of wealth. They thought it cleans the whole body. Traditional Chinese doctors also use it. Curcuma has been valued for thousands of years in India because of its benefits, so it is not surprising that most research was conducted there, exploring the main ingredient - the curcumin. Turmericor curcuma has a pleasant taste and aroma but tastes bitter in large quantities.
A silver-grey trace element belonging to the transition metals. Naturally occurring manganese compounds were used as dyes in prehistoric times. 90% of the extracted manganese is used in steel production, making it an economically important element. Manganese is a constituent of many enzymes and cardinal for photosynthesis, so biologically important. The human body contains between 10 and 20 mg of manganese, which is stored in the bones, among other things. It is essential for the physiological functioning of many processes in the human body and is necessary for the proper functioning of several important enzymes. Manganese contributes to the maintenance of normal bones and the normal formation of connective tissue.
Vitamin C is probably the best known vitamin and belongs to the group of water-soluble vitamins. While most animals can synthesize their own vitamin needs, humans must resort to dietary sources. Nutrients of animal sources contain very little Vitamin C, while green plants and fruit provide most of our vitamin C supply. Some plants contain particularly large quantities, for example 1-2 % of the dry weght of rosehip is vitamin C. In its pure form, Vitamin C was first isolated by Albert Szent-Györgyi who found it in adrenal glands in 1928. In 1931, he identified them in lemon juice and bonnet pepper. Szent-Györgyi was awarded Nobel Prize in Medicine for this discovery in 1937.
Main natural sources
Citrus fruit, berries, green and leafy vegetables, tomato and pepper.
|
|
Why is Vitamin C important?
|
|
Vitamin C contributes to our energy-producing metabolic processes, to the maintenance of normal psychological function, to the operation of the nervous and the immune systems. It also helps the formation of collagen and because of this, it maintains healthy skin, blood vessels, cartilage, bones, teeth and gums. It helps reduce fatigue, contributes to regenerating the reduced form of vitamin E and increases the absorption of iron. It contributes to the protection of cells against oxidative stress, and to the normal function of our immune system during or after intense exercise.
Vitamin D belongs to the group of fat-soluble vitamins. Vitamin D3 is produced from the dehydrocholesterol produced by the liver by the action of sunlight on the skin. Vitamin D is formed when sunlight hits skin. Ultraviolet rays convert the steroids within the skin to vitamin D. The kidneys and the liver complete the positive effect of the ultraviolet rays and give the opportunity for vitamin D to exert its activity and to transform into its active form. Some prefer to consider vitamin D as a hormone - one of those substances which is produced by the endocrine glands.
Main natural sources
Fish oil, sardines, herring, tuna, salmon, milk and diary products.
|
|
Why is Vitamin D important?
|
|
Vitamin D helps maintain normal calcium level in blood and the normal absorption and utilization of calcium and phosphor. Phosphor is involved in the maintenance of healthy bone structure. Vitamin D plays a role in cell division, helps the maintenance of healthy muscles, bones and teeth. It also helps the normal function of the immune system.
It is a fat-soluble vitamin. In its natural from, Vitamin K2 can be found in food produced by bacterial fermentation, for instance in aged cheese. It can also be found in food of animal origin, for example goose liver, goose thigh and chicken liver. Vitamin K has a role in normal blood clotting and healthy bones.


This Two Different Products contains six different types of microflora in an increased number of germs, as well as Inulin improving efficiency.
Inulin and microflora
Microflora is formed by beneficial, living microorganisms, which survive the acidic environment in the gastrointestinal tract and help maintain the balance of healthy intestinal mircroflora. Our products contain high numbers of bacterial florea and inulin which helps their reproduction. Probiotics word also known as microflora is of Greek origin meaning life. R. B. Parker was the first who used the term probotic in 1974 for organisms and substances responsible for the balance of intestinal tract. The characteristiscs of probiotics are: human origin, non-pathogenic, resistant to the digestive effects of gastric acid, bile, saliva, pancreatic and intestinal fluids. They retain their resilience in food shelf life and technological processes. In addition, probiotics are capable of adhering to mucosal cells, have antimicrobial activity against potential pathogens, and reduce the adherence of pathogenic microbes to the mucosal surface. Probiotics are mostly lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Most of the best-known probiotic lactic acid bacteria strains are Lactobacillus, smaller portion is Streptococcus genus. Prebiotics are natural nutrients, that are the sole nutrients of probiotics therefore promote their reproduction and prevalance. In the oral cavity and the gastrointestinal tract, the digestive enzymes do not break down the prebiotics and thus can reach the large intestine undigested. Prebiotics are dietary fibers, but water-soluble, therefore one of the best dietary fibers. In addition to their function of dietary fiber, their real utility lies in the fact that they are the exclusive nutrients of probiotics. Because of the lack of digestible nutrition in the large intestine where there is little food, the consumed prebiotics offer the possibility of the reproduction of human-friendly intestinal bacteria. Many foods contain prebiotics, for example: Jerusalem artichoke, chicory, onions, garlic, leeks, artichokes, whole grains, wheat, banana, flax, spinach, cabbage, chard, mustard, berries, legumes, milk and most mature cheese. Inulins are a type of prebiotics and actually dietary fibers that reach the large intestine undigested, enhance the reproduction and prevalance of probiotics. Their role: digestion, balance of the intestinal flora
Our bodies are connected with the outside world through our intestinal system that is about 7-9 meters in length (the largest area in our body). Therefore it is vulnerable by the potential attack of pathogens and toxic substances. Normally there are about 200 to 400 different types of bacterial strains in our bowels. In fetal life beneficial bacteria dominates in 95-98%. Healthy intestinal flora provides protection against a variety of pathogens, ensures the integrity of intestinal mucosa and helps the absorption of the needed nutrients. They produce many essential vitamins for our body. If the gastrointestinal tract's defense mechanisms weaken, it can cause intereference in the absorption processes. In order for probiotics to be effective in their environment, a large number is required which is at least 108 c.f.u./gram in the body. | What does the c.f.u. expression mean? c.f.u.: colony-forming units per milliliter, the number of viable microorganisms. The amount of bacteria is usually measured this way in products. However, inulin is given in milligram. As appropriate doses of at least 109 c.f.u. is accepted. | |
| What kind of probiotic products are effective? - | Prebiotics help the reproduction of probiotics, therefore products should contain inulin or fructo- oligosaccharides. | | - | They resist the effects of stomach acid, bile and digestive enzymes, so the live beneficial bacteria can reach the large intestine, where they are able to adhere and reproduce. One essential condition is that the bacteria keep their viability during their passage through the gastrointestinal tract. | | - | A good probiotic product should contain at least 5-6 strains, as we intend to make up the intestinal flora's multi-culture. | | - | During the warranty period and during technological processes they keep power of resistance. | | - | It contains of an appropriate volume of germs, the minimum quantity proposed by
specialist is 108 or 109 c.f.u. |
| |
|